Image processing is a method to convert an image into digital form and perform some operation on it, in order to get an enhanced image or to extract some useful information from it. An image can be defined as two dimensional function f(x,y) , where x and y are spatial coordinates and the amplitude of f at the coordinates (x,y) is called gray level or intensity of that point. We call an image as a digital image if (x,y) and the amplitude of f are all finite and discrete quantities. Basically there are three steps in image processing. Importing the image, analyzing and manipulating the image including data compression and image enhancement and finally get the output altered image or report.| image source
Image processing is used in various applications such as Medical imaging, Remote sensing, Textiles, Military, Film industry, Document processing etc. Versatility, Repeatability and the Preservation of original data precision are the main advantages of digital image processing methods. The various image processing techniques are
⦁ Image acquisition - to acquire a digital image⦁ Image pre-processing – improve the image to increase the chances for success the other processes
⦁ Image enhancement – improve visual impact
⦁ Image segmentation – partitions the image into parts
⦁ Image representation – convert the input data to form a suitable for computer processing
⦁ Feature extraction – extract features in synthetic aperture radar images
Image Formation
There are two parts to the image formation process. They are geometry of image formation and the physics of light. geometry of image formation determines where in the image plane the projection of a point in the scene will be located and physics of light determines the brightness of a point in the image plane as a function of illumination and surface properties.
Simple model of image formation
The scene is illuminated by a single source and reflects radiation towards the camera. The camera senses it via chemicals on film.
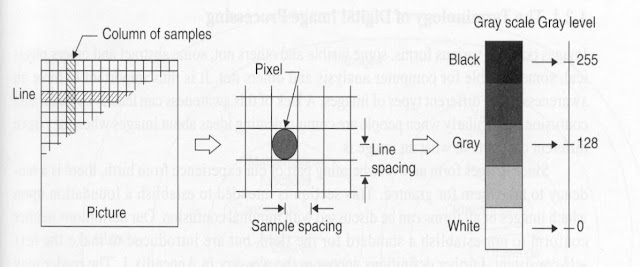
Sampling and Quantization are the two different image digitization processes in image processing. Sampling measures the value of an image at a finite number of points. Quantization is the representation of the measured value at the sampled point by an integer.
Image Enhancement
goals of Image enhancement are Suppress undesired distortions, Emphasize and sharpen image features for display and analysis. Spatial domain method and Frequency domain method are the classification of image enhancement method.
Image Analysis
Image Analysis manipulate image data to determine exactly what information is required to develop a computer imaging system. It can be broken into three primary stages. They are Preprocessing, Data reduction and Feature analysis. Data reduction involves reducing the data in the spatial domain or frequency domain. Preprocessing makes data reduction and analysis task easier. It consist of Noise and artifact removal , Extracting Region of Interest (ROI), Performing mathematical operations, Enhancement of specific image features, Data reduction in resolution and brightness
Image Compression
image compression is used to reduce the amount of data required to represent a digital image. It is very important for the image storage and image transmission. There are many applications in image compression.
Applications Of Digital Image Processing
⦁ Document scanner App for mobile phones - When a photo of a document is taken, it should be able to correct perspective warping and convert to black and white.
⦁ Removing straight lines - remove thin and nearly straight lines from image
⦁ Textile Boundary Extractor
⦁ Automatic License Plate Detection - localize license plates in images of car rears.
⦁ Extracting Urban Areas In Aerial Images - to extract urban areas in aerial images captured from Google Maps by a simple screenshot
⦁ Detecting Template In Image - to determine the position of all instances of a given template in an image.











0 Comments